
After the computer finds an Ethernet address, he stores it in its ARP cache (ARP table), so he won't need to look for it the next time he wants to send a datagram to the same address. After rreceiving the reply, the asking computer can get the Ethernet address of the computer it is looking for, from his reply. Every computer, received that request compares the requested address with its own IP address and if they match, it sends an ARP reply back to the asking computer. The broadcast-datagram sent by ARP contains a request for the IP address. When ARP wants to know whats the Ethernet address matching a given IP address it uses an Ethernet technic, called BROADCASTING, with which the datagram is addressed to all the workstations in the network. What ARP does is exactly what most people do, when they have to find Mister X in a crowd of people - they shout loud enough, so that everyone can hear them and expect Mister X to answer, if he is there.
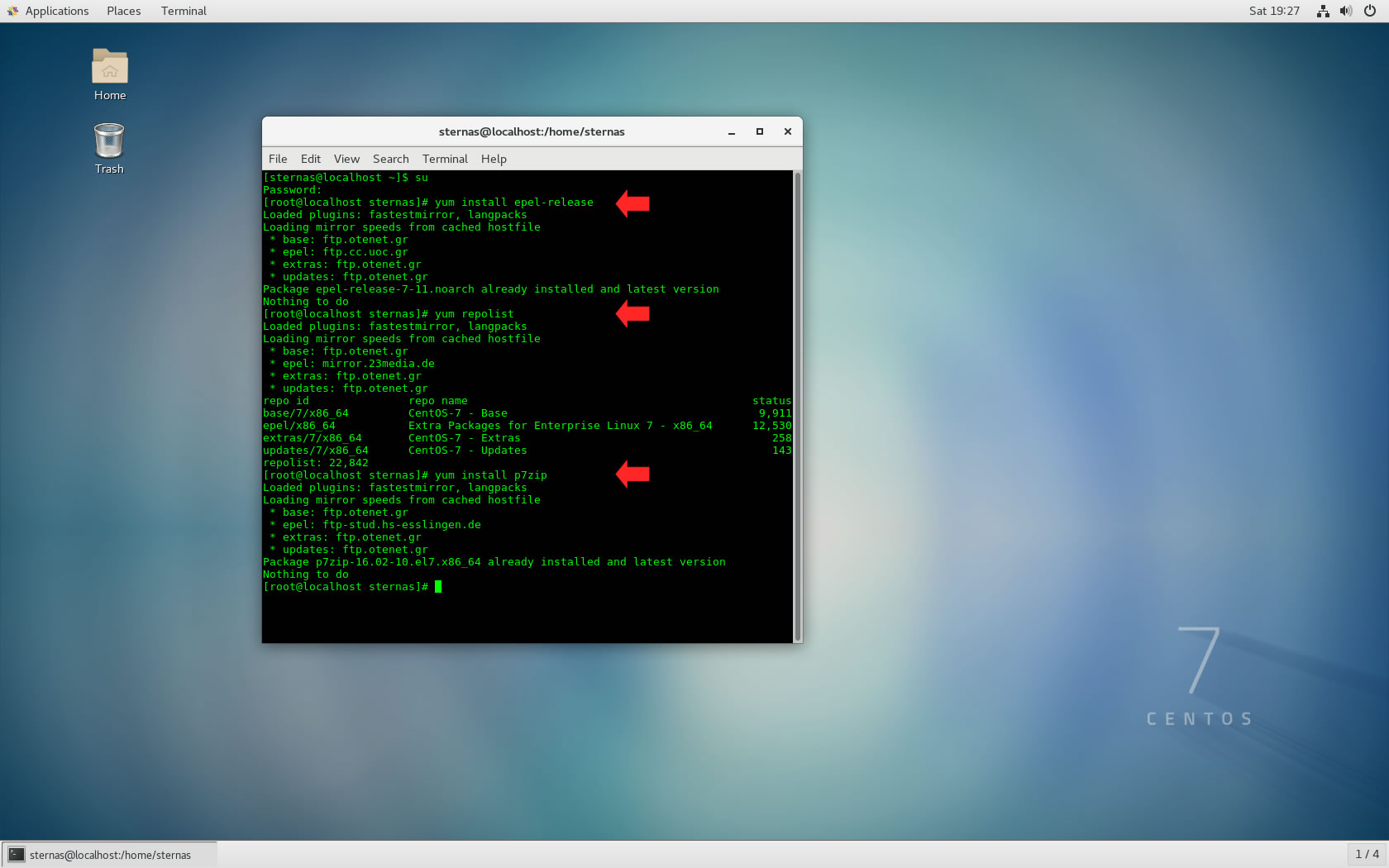
The mechanism is called ARP (Address Resolution Protocol). So, there is a mechanism needed for matching of IP addresses with the addresses in an ethernet network. In an Ethernet network computers communicate with each other via Ethernet (MAC (Media Access Control)) addresses.
Defend against UDP isc.org DNS query DDOS.Previewing your site before making DNS changes.Optimize and Tune Nginx for performance.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
